The review enforcing the new regulatory requirements, taking into account the lessons of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, requires redundant, diverse supplies of power. As instructed by electric utility companies, we have applied measures such the installation of gas-turbine-driven generators and the utilization of tertiary DC batteries to improve the supply of power to facilities.

DC 125V storage batteries

Emergency switching box connection equipment
(Source: Nuclear Regulation Authority website)
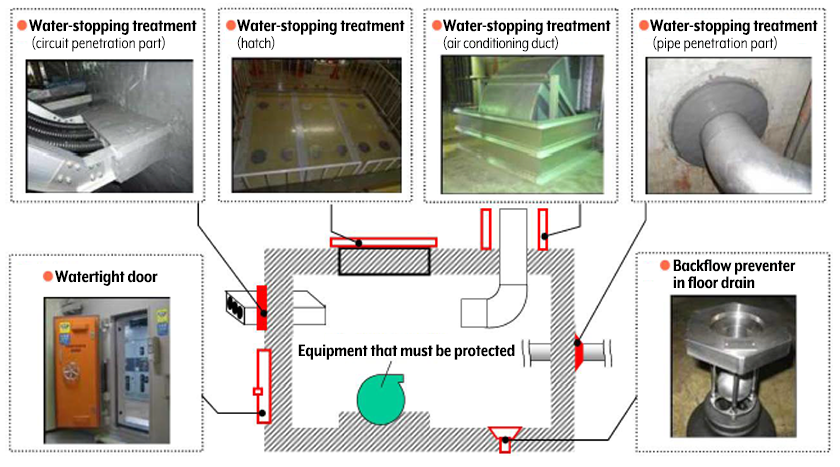
"Internal inundation measures” are required, to conform to the new regularity requirements.
These measures include water-stopping treatments (circuit penetration parts, hatches, air conditioning ducts, pipe penetration parts, etc.) and watertight doors. As instructed by electric utility companies, we have installed internal inundation measures.
(Source: Nuclear Regulation Authority website)
High Pressure Alternate Cooling System (HPAC) are installed for redundancy to replace RCIC systems when the pressure inside the RPV is high.
GVH received the contract and delivered pumps. GVH and we jointly applied this measure.
Alternate circulation cooling systems are installed to ensure redundant nuclear reactor recirculation cooling to prevent the vessel from overpressurizing or overheating.
Currently, this cooling system is preferred over a filter vent.
Filter vents (FV) are installed to prevent PCV breakdown, reduce radioactive emissions to the environment, prevent the explosion of hydrogen by releasing the hydrogen in the vessel, and transfer heat in the vessel to the atmosphere.
Filter vents have been prepared under a joint development project including AREVA and us.
This door shuts when the BOP blows out to reduce the exposure of the operators in the central control room during a severe accident.

Slide-type closure device
Corium shields have been installed to prevent the flow of corium to the drywell sump and reduce the erosion of the concrete at the bottom of RCCV, even when melted fuel has damaged the bottom of the RPV and dropped to the bottom of RCCV during a severe accident.
The plate-type heat exchanger enables cooling when the alternate circulation cooling system is used, as an emergency backup means of cooling.
The plate-type heat exchanger is a compact heat exchanger developed jointly by us and Hisaka Works.
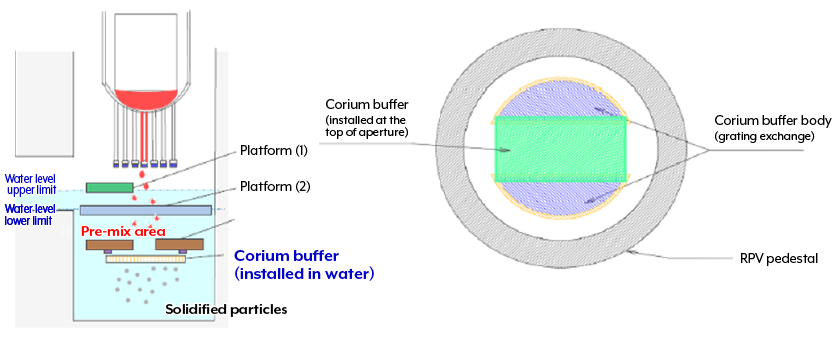
Corium buffers are buffer plates that catch debris from the RPV when the reactor core is damaged.
Nuclear business operators are considering installing them voluntarily under the new regulatory requirements.